Lysine
Last update 2022-05-27
Lysine Fermentation Engineering
98.5% L-Lysine process description
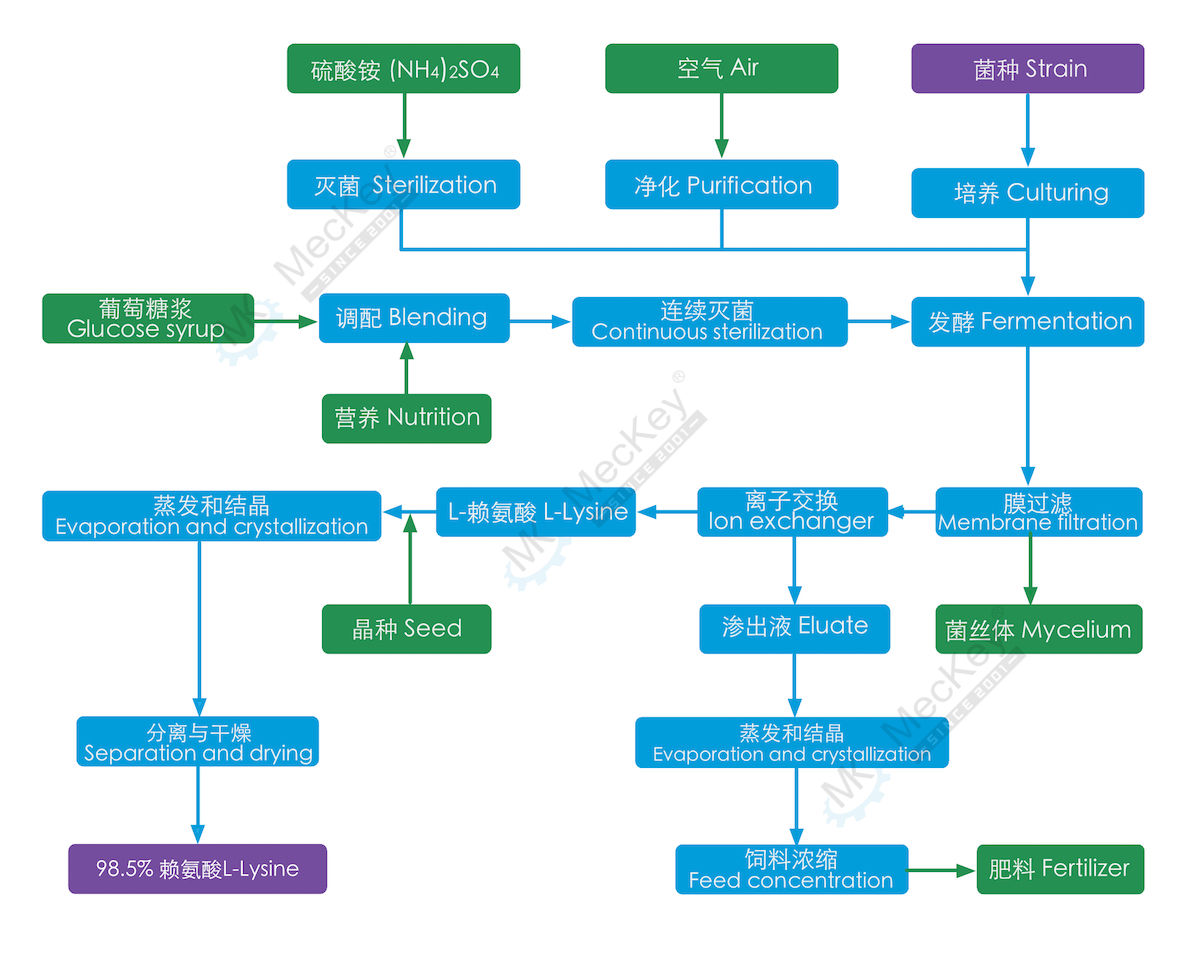
(1) Material blending: Add auxiliary materials like CSL, molasses, salt, etc. to the glucose. The material is sent to fermentation tanks after continuous sterilization during L-Lysine processing.
(2) Air preparation: Raw air must be cleaned via multi-stage filter to ensure the quality of the air to fermentation. Oil-free screw air compressors should be applied.
(3) Strain preparation: L-Lysine strain is corynebacterium glutamicum. It is selected and passed 45 hours culturing.
(4) Seed preparation: The medium is prepared then sent to flask for further culturing of slant seed. The last culturing happens in seed tank with aid of air and hydrolisate, then it is ready for fermentation.
(5) Fermentation: Production of L-Lysine takes place in special fermentors under the condition of aeration, temperature and pH. Sterile glucose syrup and ammonium sulfate solution as well as defoam reagent are added continuously to help.
(6) Mycelium separation: L-Lysine solution PH will be adjusted after fermentation. Through micro-filtration, the mycelium will be separated out for making nutrious feed.
(7) Decolorization: The L-Lysine solution will be sent to decolor tank in which the active carbon is added. After keeping agitation for 30-40minutes, the foreign color is absorbed by the carbon then the solution is sent to filter for removing dirty carbon.
(8) Ion exchange: The solution contains small qty. of positive and negative ions like Fe, Mg, Ca and Cl, SO3, etc., these items will be removed by resins with different functions in ion exchange system. Then the solution is purified.
(9) Concentration and crystallization: Concentration of the eluate from ion exchanging system is sent to vacuum evaporator&crystallizer to increase solid content for drying.
(10) Separation and drying: Concentrated L-Lysine is sent to separator to get wet crystallized L-Lysine and mother liquid. The mother liquid is partially recycled to improve yield of final product. Unrecoverable mother liquid will mix with mycelium as feed. Then the wet L-Lysine is sent to flash or fluid bed dryer for removing remaining moisture until final requirement.
65% L-Lysine process description
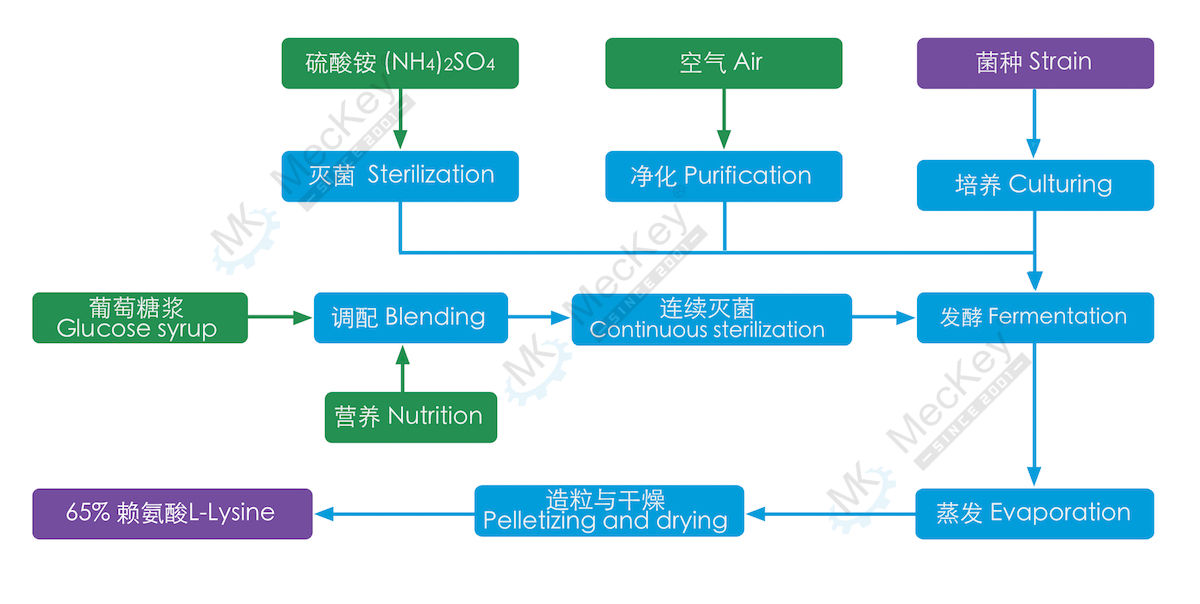
(1) Material blending: Add auxiliary materials like CSL, molasses, salt, etc. to the glucose. The material is sent to fermentation tanks after continuous sterilization during L-Lysine processing.
(2) Air preparation: Raw air must be cleaned via multi-stage filter to ensure the quality of the air to fermentation. Oil-free screw air compressors should be applied.
(3) Strain preparation: L-Lysine strain is corynebacterium glutamicum. It is selected and passed 45 hours culturing.
(4) Seed preparation: The medium is prepared then sent to flask for further culturing of slant seed. The last culturing happens in seed tank with aid of air and hydrolisate, then it is ready for fermentation.
(5) Fermentation: Production of L-Lysine takes place in special fermentors under the condition of aeration, temperature and pH. Sterile glucose syrup and ammonium sulfate solution as well as defoam reagent are added continuously to help.
(6) Concentration and crystallization: Concentration of the eluate from ion exchanging system is sent to vacuum evaporator&crystallizer to increase solid content for drying.
(7) Separation and drying: Concentrated L-Lysine is sent to separator to get wet crystallized L-Lysine and mother liquid. The mother liquid is partially recycled to improve yield of final product. Unrecoverable mother liquid will mix with mycelium as feed. Then the wet L-Lysine is sent to flash or fluid bed dryer for removing remaining moisture until final requirement.
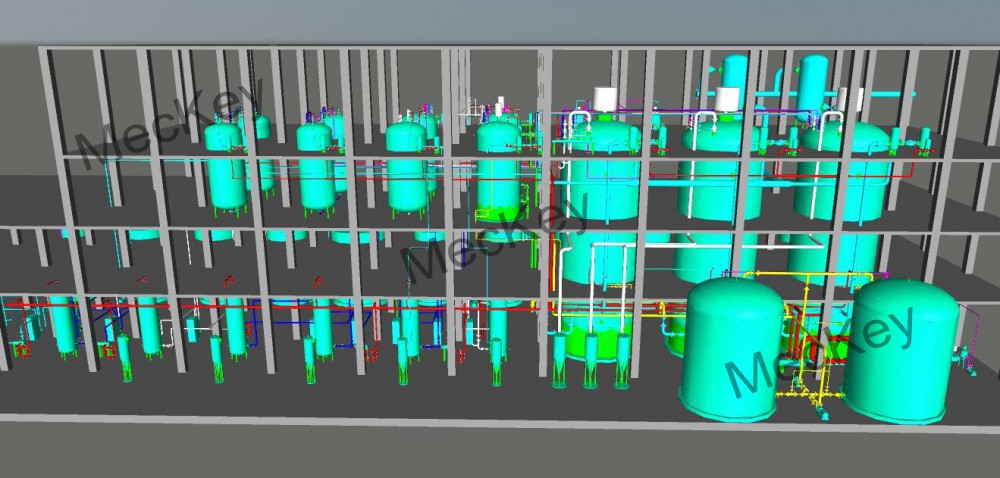
Plant 3D drawing